Testing OpenSolr Vector Search
Testing OpenSolr Vector Search: Step-by-Step Guide
This tutorial will show you how to test and explore your OpenSolr Vector Search Engine with real examples, including API queries, curl commands, and code snippets in PHP, AJAX, and Python.
1. Overview
OpenSolr lets you build a complete AI-powered search pipeline:
Crawl → Index → Embed → Solr → Search
You can create this entire flow out of the box using the OpenSolr Web Crawler Site Search Solution:
For setup details, assistance, or pricing information, contact us at:
📧 support@opensolr.com
2. Testing Vector Search Online
Test it first here with these example queries:
This will also match a concept rather than a semantic query, and in every one of these examples, or in any of our Demo Search Pages, you also get dev tools, and comprehensive stats.
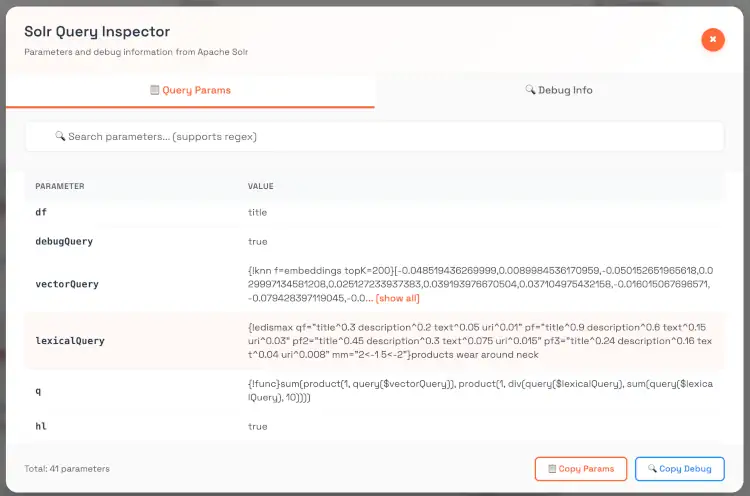
Query Paramters Inspector & DebugQuery

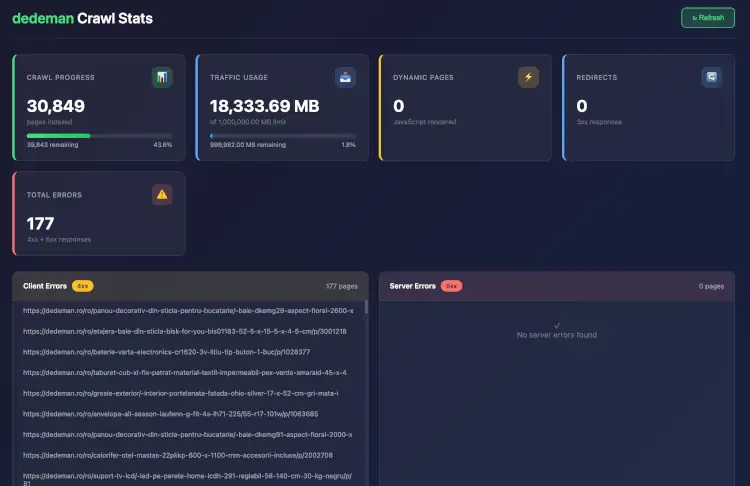
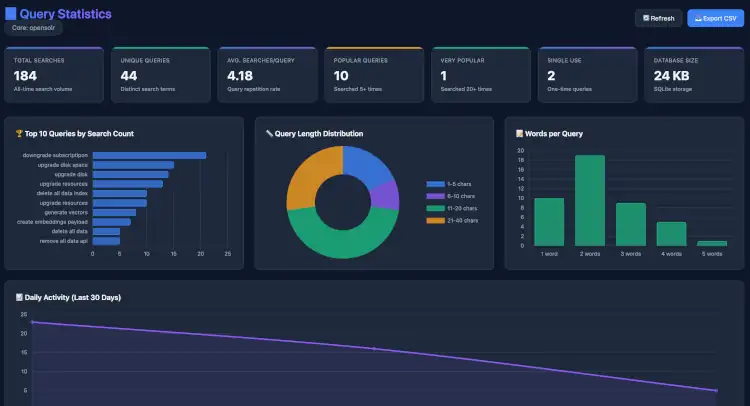
Full Crawl Stats & Search Stats for your Opensolr Web Crawler Index
You can play around with the Solr API
- ⚠️ If you know what you are doing, or else learn more here:
https://fi.solrcluster.com/solr/rueb/select?wt=json&indent=true&q=*:*&rows=2 https://chicago96.solrcluster.com/solr/peilishop/select?wt=json&indent=true&q=*:*&rows=2
For both, you can use:
Username: 123Password: 123
You can also test your vector search engine directly here:
Try using conceptual queries (semantic rather than literal):
climate disasters hurricanes floods wildfiresspace exploration mars colonization economyancient microbes life beyond earth
These queries will show how your embeddings and vector similarity work in practice.
3. Using the Solr API Directly
Solr Core Example:
https://de9.solrcluster.com/solr/vector/select?wt=json&indent=true&q=*:*&rows=2
Username: 123
Password: 123
3.1 Simple Lexical Query
curl -u 123:123 "https://de9.solrcluster.com/solr/vector/select?q=climate+change&rows=5&wt=json"
3.2 Pure Vector Query (KNN)
curl -u 123:123 "https://de9.solrcluster.com/solr/vector/select?q={!knn%20f=embeddings%20topK=50}[0.123,0.432,0.556,...]&wt=json"
Replace the vector array with your own embedding from the OpenSolr AI NLP API.
3.3 Hybrid Query (Lexical + Vector)
curl -u 123:123 "https://de9.solrcluster.com/solr/vector/select?q={!bool%20should=$lexicalQuery%20should=$vectorQuery}&lexicalQuery={!edismax%20qf=content}climate+change&vectorQuery={!knn%20f=embeddings%20topK=50}[0.12,0.43,0.66,...]&wt=json"
This version mixes traditional keyword scoring with semantic similarity — best of both worlds.
4. Getting Embeddings via OpenSolr API
You can generate embeddings for any text or document using these API endpoints:
Example:
function postEmbeddingRequest($email = "PLEASE_LOG_IN", $api_key = "PLEASE_LOG_IN", $core_name = "PLEASE_LOG_IN", $payload = "the payload text to create vector embeddings for") { $apiUrl = "https://api.opensolr.com/solr_manager/api/embed"; // Build POST fields $postFields = http_build_query([ 'email' => $email, 'api_key' => $api_key, 'index_name' => $core_name, 'payload' => is_array($payload) ? json_encode($payload) : $payload ]); $ch = curl_init($apiUrl); curl_setopt_array($ch, [ CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER => true, CURLOPT_POST => true, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS => $postFields, CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER => [ 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' ], CURLOPT_TIMEOUT => 30, CURLOPT_CONNECTTIMEOUT => 10, ]); $response = curl_exec($ch); $httpCode = curl_getinfo($ch, CURLINFO_HTTP_CODE); $error = curl_error($ch); curl_close($ch); if ($error) { error_log("cURL error: $error"); } if ($httpCode < 200 || $httpCode >= 300) { error_log("HTTP error: $httpCode - Response: " . ($response ?: 'No response')); } if (empty($response)) { error_log("Empty response from API."); } $json = json_decode($response, true); if (json_last_error() !== JSON_ERROR_NONE) { error_log("Failed to decode JSON response: " . json_last_error_msg()); } return $json; }
Response will include the vector embedding array you can pass to Solr.
5. Example Implementations
PHP Example
<?php $url = 'https://de9.solrcluster.com/solr/vector/select?wt=json'; $query = '{!bool should=$lexicalQuery should=$vectorQuery}'; $params = [ 'lexicalQuery' => '{!edismax qf=content}climate disasters', 'vectorQuery' => '{!knn f=embeddings topK=50}[0.12,0.43,0.56,0.77]' ]; $ch = curl_init($url); curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_USERPWD, '123:123'); curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, http_build_query($params)); curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true); $response = curl_exec($ch); curl_close($ch); echo $response; ?>
AJAX Example
<script> fetch('https://de9.solrcluster.com/solr/vector/select?wt=json&q={!knn%20f=embeddings%20topK=10}[0.11,0.22,0.33]', { headers: { 'Authorization': 'Basic ' + btoa('123:123') } }) .then(r => r.json()) .then(console.log); </script>
Python Example
import requests from requests.auth import HTTPBasicAuth url = "https://de9.solrcluster.com/solr/vector/select" params = { 'q': '{!bool should=$lexicalQuery should=$vectorQuery}', 'lexicalQuery': '{!edismax qf=content}climate disasters', 'vectorQuery': '{!knn f=embeddings topK=50}[0.12,0.43,0.56,0.77]', 'wt': 'json' } response = requests.post(url, data=params, auth=HTTPBasicAuth('123', '123')) print(response.json())
6. Notes
- You can adjust
topKto control how many similar results you want (usually 20–100). - If you use
{!bool should=should}instead ofmust, the vector similarity will have more influence on ranking. - For best hybrid results, combine both lexical and vector queries.
7. Need Help?
To get started or request a ready-to-use search engine setup:
📧 support@opensolr.com













